Often promoted as a miracle crop, industrial hemp’s value chain is far reaching and many possible applications yet remain vastly untapped. Below we break down some of the most promising applications of the hemp’s biomass, primarily of the hemp’s stalk which contains hemp fibers and hemp hurds, the inner ‘woody parts’ of the stalk.
Why Industrial Hemp?
Hemp is one of the most resistant, absorbent and durable fibres
of vegetable origin. It is now emerging as a commodity mature enough to not only impact, but possibly revolutionize tech-driven markets and economies around the world. With its diversified use, hemp offers a surprisingly versatile solution to todays and future challenges.
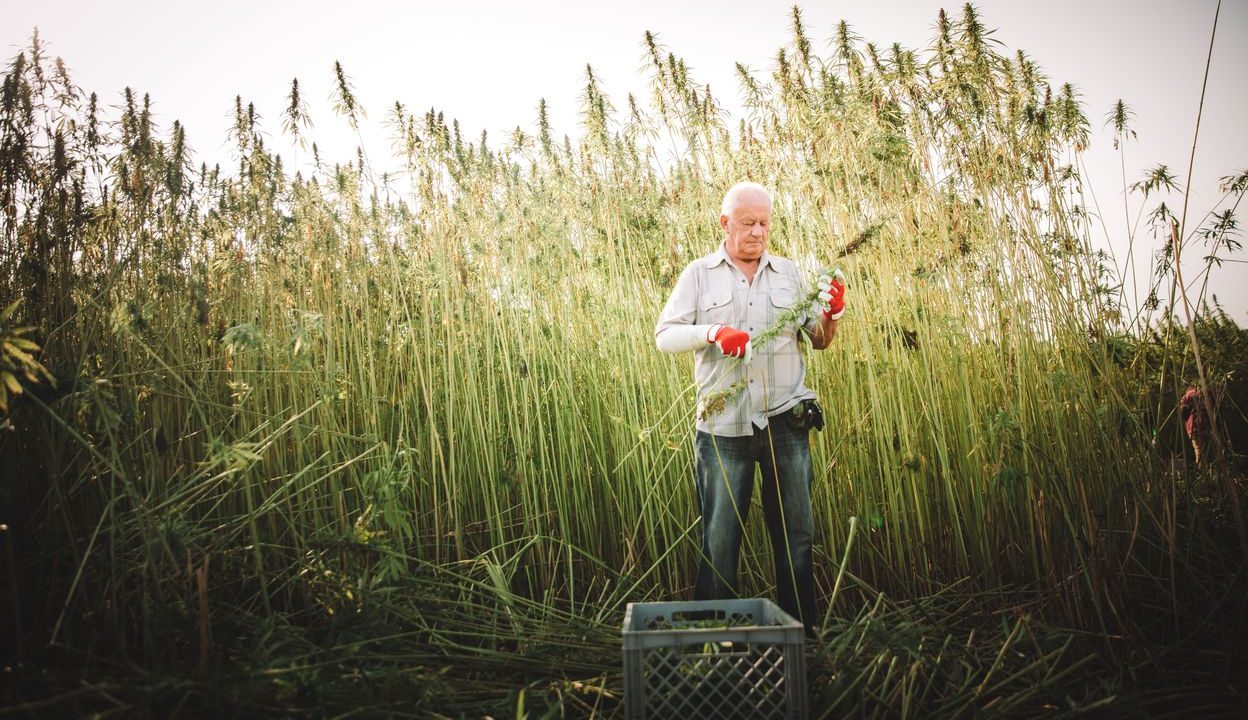


Photo – Hempoint
History of Hemp
Industrial hemp, known as Cannabis sativa L., the non-psychoactive relative to cannabis indica, was used by mankind for thousands of years. For ropes, paper, food and medicine. It is in fact a new old crop. It was probably the earliest plant cultivated and spun into usable textile grade fiber. It is believed that hemp made it to Europe in approximately 1,200 BC. From there, it spread throughout the ancient world. China appears to have the longest continuous history of Hemp cultivation (over 6000 years). For a reason we call it an ancient crop for modern-day challenges.
Fast forward to 1961: Cannabis flowers ended up scheduled as a drug on the UN Single Convention document and cultivation of all cannabis plants became internationally prohibited. Industrial use and purpose of production only for fiber and seeds was exempted. French breeders created varieties with 0,2% THC levels.
The EU catalog currently lists 75 different varieties from across Europe which are legal to grow in all EU states for industrial purposes. Some countries around the world made special regulations for legal growth of industrial hemp so there are still places where everything from hemp is still illegal.
Nature-based solution with a business model.
Applications
Carbon negative construction industry?

Construction
We can’t recycle our way out of the problem.

Plastics & Composites
Wearing the change.
Textiles
Let’s turn over a new leaf.

Pulp and paper
Power of nature as fuel or energy storage.

Energy
Nutrient powerhouse for humans and animals.

Food
Essential compounds for body homeostasis.

Phytocannabinoids
Hemp can do so much more.

Environmental services
Climate Change Context
We’ve appearently crossed the line.
Recently, humanity crossed a threshold of 420 ppm (parts-per-million) of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere. The health of the ecosystems on which we and all other species depend is deteriorating more rapidly than ever. Climate change threatens people all over the world with food and water scarcity, increased flooding, extreme heat, more disease, and unprecedented economic loss. Vast majority of scientists agree that human activity is “the main driver of climate change”.
There is no silver bullet when it comes to tackling climate change.
Let’s be honest – there are hundreds of innovative solutions to climate change, as well as sources where to read about them. Project Drawdown is a good starting point, listing some of the most promising ones. While hemp is missing in the list, its rapidly growing biomass and wide range of industrial applications can play its role as a potent carbon sink. Hemp is, in fact, one of the fastest CO2-to-biomass conversion tools available. Hemp fibers and hurds can replace a wide range of products in some of the most polluting industries.


Photo ― Unsplash
Hemp for Sustainable Development Goals.
We believe hemp is an important instrument to help fulfill the UN 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. Below you can find some of the goals (7.,8.,9.,11.,12.,13.,15.) where hemp is most relevant and beneficial. In 2019, our team members also helped put together the Cannabis and Sustainable Development publication.
Bioeconomy, EU Green Deal
What’s our vision?
To make industrial hemp- primarily the environmental benefits of hemp agronomy and the use of it biomass – hemp fibers, hemp hurds – recognized as a valuable part of the bio-economy strategies and other policy papers such as the EU Green Deal.
Bio-economy as the new norm.
Industrial hemp fits perfectly into the action plan proposed by the European Commission that aims to improve and scale up the sustainable use of renewable bio-based resources to address global and local challenges such as climate change and sustainable development.
The Real Green Deal.
The EU Green Deal is a new growth strategy that aims to transform the European Union into a modern, resource-efficient and competitive economy and the first climate-neutral continent through investing in environmentally-friendly technologies, supporting industry to innovate, decarbonizing the energy sector, ensuring buildings are more energy efficient, etc.
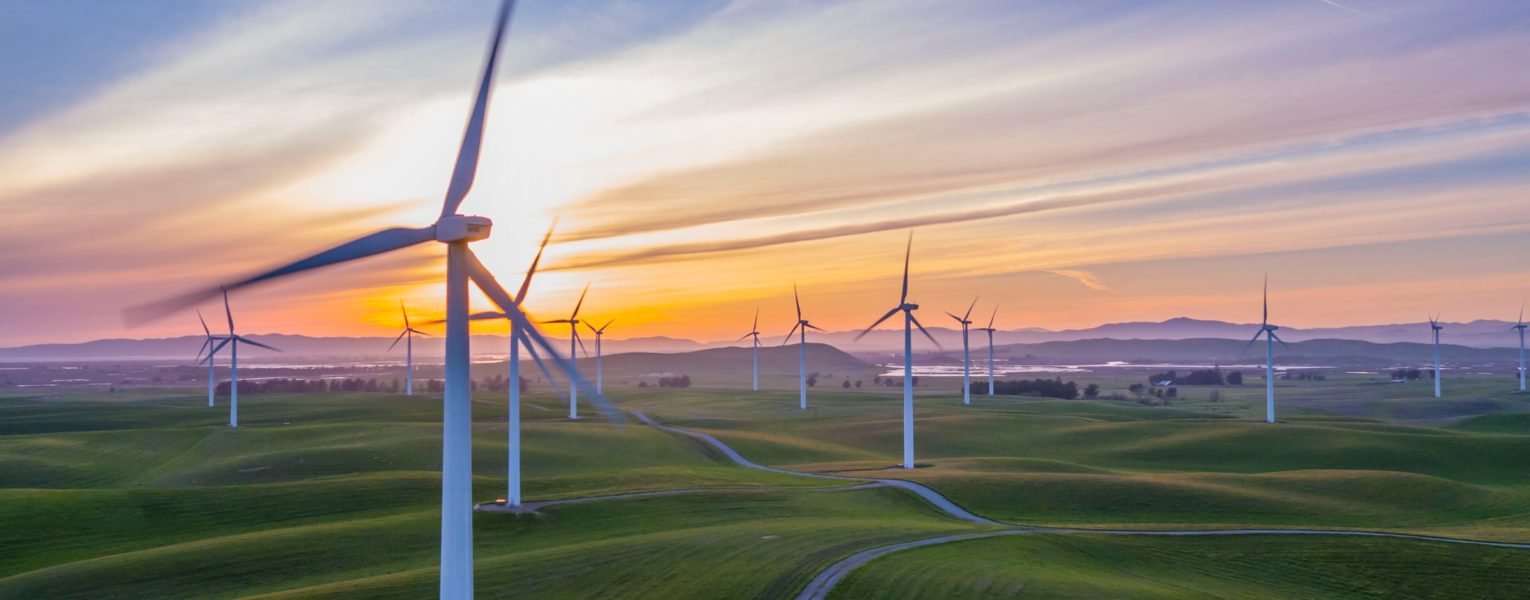


Photo – Unsplash